OTHER PROJECTS
RESEARCH PROJECTS OF DELOGU'S LAB:
SEE - H2020-MSCA-GF
Two-dimensional (2D) transition metal carbides/carbonitrides (MXenes), discovered by the outgoing phase Supervisor, Yury Gogotsi (H-index = 160), at Drexel University (USA), have stepped into the limelight of 2D materials (2DMs). Within the SEE project, the Fellow, Dr. Laura Fusco, will learn to produce and characterize MXenes from the most recognized leader in the field. SEE will provide a thorough evaluation of the skin impact and possible immunomodulation of a wide variety of MXenes. No study has investigated at the same time and on a large scale these key aspects for MXene safety and effective use as bioelectronics or biomedical tools applied to the skin. The outstanding peculiar scientific expertise of the Fellow, relying on the characterization of 2DM effects at the skin level depending on their physicochemical properties, will be essential to achieve the project goals. The European Fellow Supervisors, Bengt Fadeel and Lucia G. Delogu, among the most influential scientists in the field of nano-immunology and toxicology, will contribute to the Fellow training by employing the most cutting edge high-dimensional technologies at the single-cell level (e.g. CyTOF, Rhapsody and Hyperion) and pioneering cell-cell analysis systems (e.g. LIPSTIC approach) in this context. The Fellow will also explore the commercial applicability of her results during a secondment at the revolutionist biotech company Fluidigm Corporation. Within SEE, the Fellow will introduce her own novel concept of “Nano-SkinImmunity-by-design”, where the analysis of the cutaneous effects when designing MXenes (and 2DMs) will not only be relevant for their safety, but will also turn them into active tools for cutaneous applications endowed of immune properties, tailorable adjusting their physicochemical profile. By exploring these crucial aspects, SEE aims at incising the strategic field of MXenes and 2DMs as well as their role in biomedicine and nanotechnology at European level and beyond.
HELICAL - H2020-MSCA-ITN
HEalth data Lnkage for CliniAL benefict (HELICAL) provides training in analysis of large datasets to elucidate the complex biology of chronic diseases. HELICAL exploits recent advances in data science to link research datasets with longitudinal healthcare records, based on the robust ethical foundation required for linkage studies using near-patient data, to address key experimental questions. The training provided addresses a key skills gap in the European workforce and should make the ESR eminently employable in academic, industrial and clinical sectors.

WHISKIES - WOUND HEALING IN SPACE: KEY CHALLENGES TOWARDS INTELLIGENT AND EABLING SENSING PLATFORMS
WHISKIES stems from the European Space Agency Topical Team Network “Tissue Healing in Space: Techniques for promoting and monitoring tissue repair and regeneration” (https://www.thm-esatt.net). Human Space Exploration has always been a powerful driving force to develop ground-breaking solutions, foundational technology, and new approaches. It is also worthy to notice that Space could be considered a unique remote environment. Solutions found for Space applications could, then, help managing problems existing on-ground for rural areas. We believe that, by taking advantage of the Space environment, WHISKIES can contribute to these efforts for a better, innovative, efficient and patient-centered health care ecosystem.

IMM-GNRs, CALL MSCA IF Horizon 2020
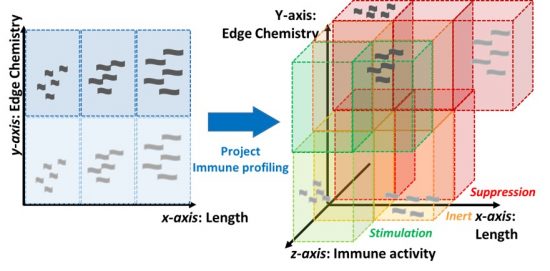
As Overall Goal IMM-GNRs intends to overcome the aforementioned limits of conventional nano-immunotoxicology approaches. IMM-GNRs will provide a comprehensive and quantitative picture of the GNRs immune activity in relation to their structural properties (shape, edge structures, width, size, molecular weight).

CARBO-IMmap, CALL RISE under Horizon 2020
The CARBO-IMmap project major aim is to advance the field of carbon nanomaterial development and their exploitation biomedical applications. The long-range goal of Carbo-IMmap is to develop a functional pipeline for the immune-characterization of carbon nanomaterials, for the qualitative and quantitative assessment in vitro and ex vivo of the human immune compatibility and immune activity of newly developed carbon materials.
The program will enable long-term, transformative research collaborations that will contribute to the integration and collaboration of research groups of 4 European Countries (Germany, Italy, France and Spain) and 3 key non-EU Countries: USA, China and Qatar.
Role: Coordinator

Multifunctional nanotool for advanced cancer diagnostics, PRIN 2016 under the Italian MIUR
The overriding goal of this research program is to develope innovative materials and explore novel strategies for the detection of tumor markers. The project will lead to the development of nanotools that, by joining the advantageous features of nanometer-scale carbon-based materials and biological recognition elements, will allow the detection of tumor markers with high sensitivity and specificity.

G-IMMUNOMICS, call FlagERA 2015 under Horizon 2020

Graphene is the most promising, versatile, and sustainable key enabling nanotechnology which may bring solutions in the near future to many areas spanning materials science and medicine.
The overall objective of G-IMMUNOMICS is to complement Flagship research on graphene safety with immunogenomic and proteomic data, not covered by the Core Project. G-IMMUNOMICS will provide new insights on the immune impact of several types of graphene to lay the basis for a safe use of graphene and the graphene technology future transfer in medicine. The specific objectives are:
1- Produce highly stable and dispersible pristine and functionalized graphene family materials (GFMs) with different lateral size and appropriate functionalizations
2- Characterize by high throughput functional immunogenomics and proteomics approaches and genotoxic assays the immune cell response induced by GFMs on different cell lines and primary cell.
3- Evaluate the immune cell response induced by GFMs on four different species: human, mouse, pig and worm.
Role: Coordinator

G-NANOULTRA: Graphene as a new nanocontrast agent for cancer ultrasonography diagnosis and therapy

Ultrasonography (US) is used in every day clinical practice. Current US contrast agents (USCAs) are exclusively diagnostic tools. We showed great potential of carbon nanomaterials as USCAs (Delogu LG et al PNAS 2012). The project G-NANOULTRA is based on a solid international network of collaborations and the expertise in nanobiotechnology of the PI. We aim at develop new carbon USCAs based on graphene with multiple functions such as: cancer diagnosis, immunotherapy and fast drug delivery.
Role: Coordinator
